Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. Understanding Children’s Mental Health
- III. Creating a Supportive Environment at Home
- IV. Building Resilience in Children
- V. Seeking Professional Help
- VI. Strategies for Coping with Stress and Anxiety
- VII. Promoting Healthy Screen Time Habits
- VIII. Supporting Your Child’s Emotional Well-being
- IX. Identifying and Addressing Bullying
I. Introduction

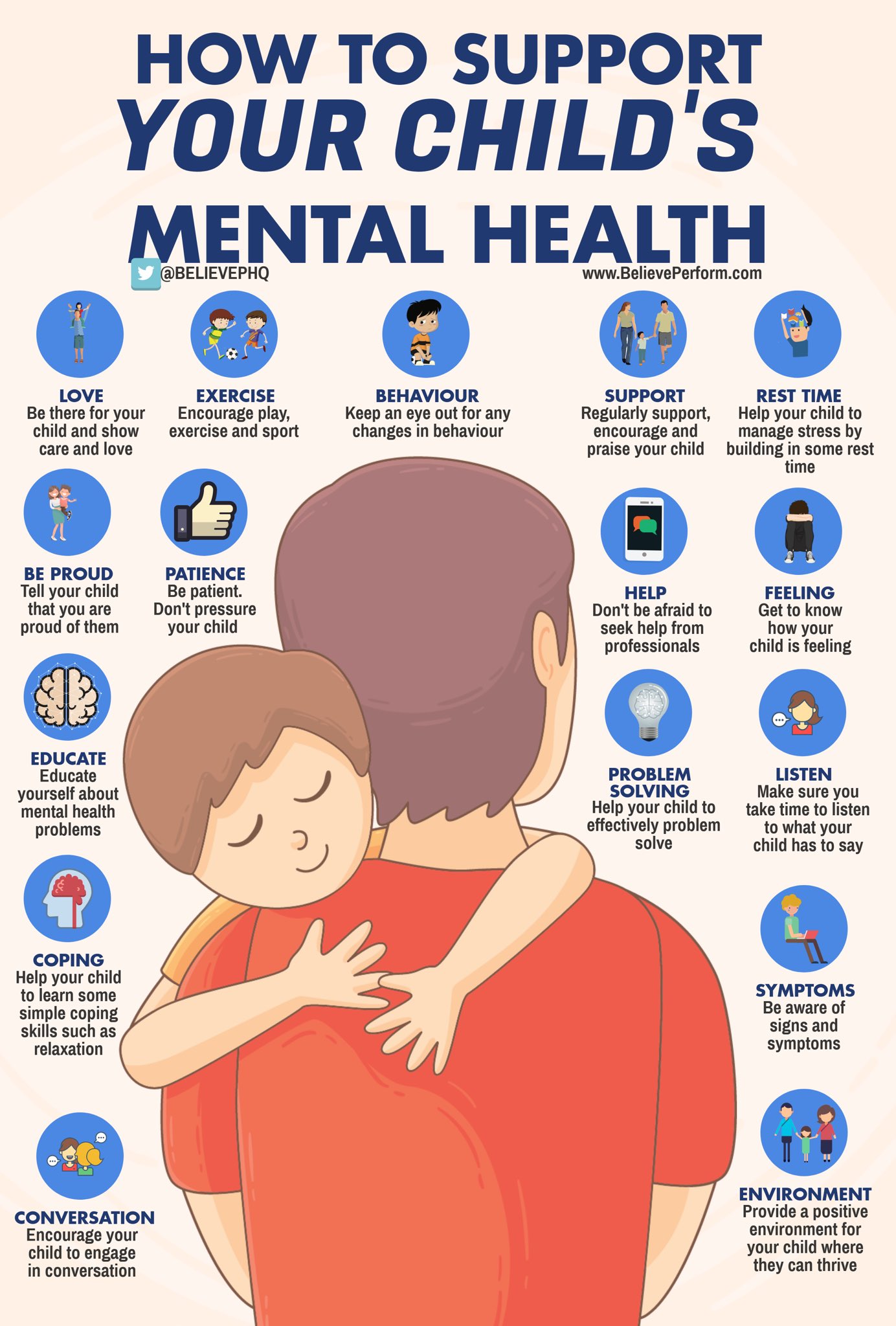
Welcome to the ultimate guide on how to support your child’s mental health. As a parent, it is essential to prioritize your child’s well-being, both physically and mentally. In today’s fast-paced and challenging world, children face various stressors that can impact their mental health. This comprehensive guide will provide you with practical tips, strategies, and resources to help your child navigate through these challenges and develop resilience.
Throughout this guide, we will explore a range of topics, including understanding the importance of mental health in children, recognizing signs of mental health issues, fostering open communication, promoting healthy habits, and seeking professional help when needed. By addressing these aspects, you will be equipped with the knowledge and tools to create a supportive environment for your child’s mental well-being.
It is important to note that every child is unique, and their mental health needs may vary. This guide aims to provide general guidance and suggestions that can be adapted to suit your child’s specific circumstances. Remember, you are the best advocate for your child, and your love and support can make a significant difference in their mental health journey.
So, let’s dive in and explore the various ways you can support your child’s mental health. Together, we can create a nurturing and resilient environment that promotes their overall well-being.
II. Understanding Children’s Mental Health
Children’s mental health is a topic that requires careful attention and understanding. As parents, caregivers, and educators, it is crucial to be aware of the common mental health issues that children may face and to recognize the signs and symptoms associated with these issues. By gaining a deeper understanding of children’s mental health, we can provide the necessary support and resources to help them navigate these challenges.
A. Common Mental Health Issues in Children
1. Anxiety disorders
Anxiety disorders are one of the most common mental health issues in children. Children with anxiety disorders often experience excessive worry, fear, and unease. They may have difficulty controlling their worries and may exhibit physical symptoms such as restlessness, irritability, and trouble sleeping. It is important to note that anxiety disorders can manifest in different ways, including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias.
2. Depression
Depression is another prevalent mental health issue in children. Children with depression may exhibit persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities they once enjoyed. They may also experience changes in appetite, sleep patterns, and energy levels. It is essential to differentiate between normal mood swings and clinical depression, as early intervention can make a significant difference in a child’s well-being.
3. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Children with ADHD may have difficulty focusing, staying organized, and controlling their impulses. They may also struggle with following instructions and completing tasks. Early identification and appropriate interventions can help children with ADHD manage their symptoms and thrive academically and socially.
4. Autism spectrum disorder (ASD)
ASD is a complex developmental disorder that affects a child’s social interaction, communication skills, and behavior. Children with ASD may have difficulty understanding and responding to social cues, may exhibit repetitive behaviors, and may have specific interests or routines. Early intervention and specialized therapies can support children with ASD in developing their communication and social skills.
B. Signs and Symptoms of Mental Health Issues in Children
1. Behavioral changes
Children experiencing mental health issues may exhibit changes in their behavior. They may become withdrawn, irritable, or agitated. They may also display oppositional or defiant behaviors, have trouble concentrating, or experience a decline in academic performance. Paying attention to these behavioral changes can help identify underlying mental health concerns.
2. Emotional changes
Emotional changes can also indicate potential mental health issues in children. They may express persistent sadness, irritability, or anger. They may have frequent mood swings or seem excessively worried or fearful. It is important to create a safe and supportive environment where children feel comfortable expressing their emotions and seeking help when needed.
3. Physical symptoms
Mental health issues can also manifest in physical symptoms. Children may complain of frequent headaches or stomachaches without any underlying medical cause. They may experience changes in appetite, sleep disturbances, or fatigue. Recognizing these physical symptoms can help identify the presence of mental health concerns.
Understanding children’s mental health is crucial for providing the necessary support and resources to help them thrive. By being aware of the common mental health issues in children, recognizing the signs and symptoms, and seeking appropriate interventions, we can contribute to their overall well-being and ensure they have the tools to navigate life’s challenges.
III. Creating a Supportive Environment at Home
Creating a supportive environment at home is crucial for your child’s mental health. As a parent, you play a vital role in shaping their well-being. Here are some strategies to establish a nurturing atmosphere:
A. Open communication and active listening
Encouraging open communication and actively listening to your child can make a significant difference in their mental health. Create a safe space where they feel comfortable expressing their thoughts and emotions without judgment. Be attentive and fully present when they talk to you, giving them your undivided attention. This will help them feel valued and understood.
When engaging in conversations, use open-ended questions to encourage them to share more about their experiences. Avoid interrupting or dismissing their feelings. Instead, validate their emotions and provide empathetic responses. By fostering open communication and active listening, you can build a strong foundation of trust and support.
B. Establishing routines and structure
Establishing routines and structure in your child’s daily life can promote stability and a sense of security. Consistent schedules help children feel more organized and in control, reducing anxiety and stress. Create a daily routine that includes designated times for meals, schoolwork, play, and relaxation.
Ensure that your child understands the expectations and responsibilities associated with each activity. This clarity helps them develop a sense of purpose and accomplishment. Additionally, having a structured routine can improve sleep patterns, which are essential for mental well-being.
C. Encouraging healthy lifestyle habits
Healthy lifestyle habits contribute significantly to your child’s overall mental health. Here are three key areas to focus on:
1. Balanced diet
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in supporting your child’s mental health. Provide them with a variety of nutritious foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid excessive consumption of sugary snacks and processed foods, as they can negatively impact mood and energy levels.
Encourage regular family meals and involve your child in meal planning and preparation. This not only promotes healthy eating habits but also strengthens family bonds.
2. Regular exercise
Physical activity is not only beneficial for physical health but also has a positive impact on mental well-being. Encourage your child to engage in regular exercise or participate in activities they enjoy, such as sports, dancing, or yoga. Physical activity releases endorphins, which are natural mood boosters.
Make exercise a fun and enjoyable experience by joining them in their activities or organizing family outings that involve physical movement. This not only promotes their mental health but also strengthens the parent-child bond.
3. Sufficient sleep
Adequate sleep is essential for your child’s mental and emotional well-being. Establish a consistent bedtime routine that allows for enough sleep based on their age. Create a calm and relaxing environment in their bedroom, free from distractions like electronic devices.
Encourage winding down activities before bed, such as reading or listening to soothing music. Sufficient sleep improves cognitive function, emotional regulation, and overall mental health.
By creating a supportive environment at home through open communication, routines, and healthy lifestyle habits, you can significantly contribute to your child’s mental well-being. Remember, your role as a parent is instrumental in shaping their overall happiness and success.
IV. Building Resilience in Children

Building resilience in children is crucial for their overall mental health and well-being. As a parent or caregiver, it is important to provide them with the necessary tools and support to navigate through life’s challenges. In this section, we will explore three key strategies for building resilience in children: teaching problem-solving skills, encouraging positive self-esteem and self-confidence, and fostering social connections and friendships.
A. Teaching problem-solving skills
One of the most effective ways to build resilience in children is by teaching them problem-solving skills. By equipping them with the ability to identify and solve problems, you are empowering them to face challenges head-on and find solutions. Here are some strategies to help teach problem-solving skills:
- Encourage critical thinking: Encourage your child to think critically and analyze situations from different perspectives. This will help them develop problem-solving skills and make informed decisions.
- Break down problems: Teach your child how to break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable tasks. This will help them approach challenges with a clear plan of action.
- Encourage creativity: Foster your child’s creativity by encouraging them to think outside the box when solving problems. This will help them develop innovative solutions and build resilience.
- Provide guidance: Offer guidance and support when your child is facing a problem. Help them brainstorm possible solutions and guide them towards making the best decision.
B. Encouraging positive self-esteem and self-confidence
Building positive self-esteem and self-confidence is essential for children to develop resilience. When children have a strong sense of self-worth, they are better equipped to handle setbacks and bounce back from adversity. Here are some ways to encourage positive self-esteem and self-confidence:
- Praise effort, not just outcomes: Instead of focusing solely on the end result, praise your child’s effort and hard work. This will help them develop a growth mindset and understand that their abilities can improve with practice.
- Set realistic goals: Encourage your child to set realistic goals and celebrate their achievements along the way. This will boost their self-confidence and motivate them to continue working towards their goals.
- Encourage self-care: Teach your child the importance of self-care and taking care of their physical and mental well-being. When they prioritize self-care, they are more likely to have a positive self-image and higher self-esteem.
- Provide a supportive environment: Create a supportive and nurturing environment where your child feels safe to express themselves and take risks. This will help them develop a strong sense of self and build resilience.
Social connections and friendships play a crucial role in building resilience in children. Having a strong support system can provide children with the emotional support they need during challenging times. Here are some ways to foster social connections and friendships:
- Encourage social activities: Encourage your child to participate in social activities such as team sports, clubs, or community events. This will help them develop social skills, build friendships, and expand their support network.
- Teach empathy and kindness: Teach your child the importance of empathy and kindness towards others. Encourage them to be inclusive and supportive of their peers, which will help them build meaningful connections.
- Model healthy relationships: Be a positive role model by demonstrating healthy relationships and friendships in your own life. Children learn by observing, so show them what it means to be a good friend and how to maintain positive relationships.
- Encourage open communication: Create an environment where your child feels comfortable expressing their thoughts and feelings. Encourage open communication and active listening, which will strengthen their relationships and support system.
By teaching problem-solving skills, encouraging positive self-esteem and self-confidence, and fostering social connections and friendships, you can help build resilience in children. These strategies will equip them with the necessary tools to navigate through life’s challenges and thrive in the face of adversity.
V. Seeking Professional Help
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1279276909-1bae9b59ebb8466f8fcde8b1a578ada4.jpeg)
Recognizing when professional help is needed is crucial in supporting your child’s mental health. As a parent, it’s important to be aware of the signs and symptoms that may indicate your child is struggling and could benefit from professional intervention.
Some common signs that may indicate the need for professional help include:
- Significant changes in behavior, such as increased aggression or withdrawal
- Difficulty concentrating or a decline in academic performance
- Intense and persistent feelings of sadness or anxiety
- Excessive worry or fear that interferes with daily activities
- Changes in appetite or sleep patterns
- Engaging in self-harming behaviors
- Substance abuse or experimentation
If you notice any of these signs or have concerns about your child’s mental well-being, it’s important to seek professional help. Early intervention can make a significant difference in your child’s overall mental health and well-being.
Types of mental health professionals for children
When seeking professional help for your child, there are several types of mental health professionals who specialize in working with children and adolescents. Each professional has a unique set of skills and expertise to address different mental health concerns.
1. Child psychologists
Child psychologists are trained professionals who specialize in assessing and treating children’s mental health issues. They use various therapeutic techniques, such as play therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and family therapy, to help children overcome their challenges.
Child psychologists work closely with children to identify and address emotional, behavioral, and developmental issues. They provide a safe and supportive environment where children can express their thoughts and feelings, develop coping strategies, and improve their overall well-being.
2. Child psychiatrists
Child psychiatrists are medical doctors who specialize in diagnosing and treating mental health disorders in children and adolescents. They have the authority to prescribe medication and provide comprehensive psychiatric care.
Child psychiatrists conduct thorough evaluations to determine the underlying causes of mental health issues and develop personalized treatment plans. They work collaboratively with other mental health professionals, such as psychologists and therapists, to provide holistic care for children.
3. Pediatricians
Pediatricians are doctors who specialize in the medical care of children, including their mental health. While they may not provide specialized therapy or medication management, they play a crucial role in identifying and addressing mental health concerns in children.
Pediatricians can conduct initial screenings, provide referrals to mental health professionals, and offer guidance and support to parents. They work in collaboration with other mental health professionals to ensure comprehensive care for children.
How to find a suitable mental health professional for your child
When searching for a suitable mental health professional for your child, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
- Qualifications and expertise: Look for professionals who have specific experience and training in working with children and adolescents.
- Approach and therapeutic techniques: Consider the therapeutic approach and techniques used by the professional to ensure they align with your child’s needs and preferences.
- Availability and accessibility: Take into account the professional’s availability, location, and scheduling options to ensure convenient access to care.
- Referrals and recommendations: Seek recommendations from trusted sources, such as pediatricians, school counselors, or other parents who have had positive experiences with mental health professionals.
- Compatibility and rapport: It’s important for your child to feel comfortable and connected with the professional. Consider scheduling an initial consultation to assess the compatibility and rapport between your child and the professional.
Remember, finding the right mental health professional for your child may take time and involve trial and error. It’s important to prioritize your child’s well-being and seek professional help when needed to support their mental health journey.
VI. Strategies for Coping with Stress and Anxiety
In today’s fast-paced world, stress and anxiety have become common issues for both adults and children. As a parent, it is essential to equip your child with effective strategies to cope with these challenges. In this section, we will explore various techniques that can help your child manage stress and anxiety.
A. Relaxation techniques
1. Deep breathing exercises:
Deep breathing exercises are a simple yet powerful technique to help your child relax and reduce anxiety. Encourage your child to take slow, deep breaths in through their nose and exhale slowly through their mouth. This practice helps activate the body’s relaxation response and promotes a sense of calmness.
2. Progressive muscle relaxation:
Progressive muscle relaxation is another effective technique for relieving stress and anxiety. Guide your child to tense and then relax each muscle group in their body, starting from their toes and working their way up to their head. This exercise helps release tension and promotes overall relaxation.
B. Mindfulness and meditation
Mindfulness and meditation are practices that can help your child cultivate a present-moment awareness and reduce stress. Encourage your child to set aside a few minutes each day for mindfulness or meditation exercises. They can focus on their breath, observe their thoughts without judgment, or engage in guided meditation sessions specifically designed for children.
C. Stress management techniques for children
1. Encourage open communication:
One of the most important stress management techniques for children is to encourage open communication. Create a safe and non-judgmental space where your child feels comfortable expressing their feelings and concerns. Listen actively and validate their emotions, helping them develop healthy coping mechanisms.
2. Promote a healthy lifestyle:
A healthy lifestyle plays a crucial role in managing stress and anxiety. Encourage your child to engage in regular physical activity, eat a balanced diet, and get enough sleep. These habits contribute to overall well-being and help reduce stress levels.
3. Teach problem-solving skills:
Teaching your child problem-solving skills empowers them to tackle stressful situations effectively. Encourage them to identify the problem, brainstorm possible solutions, evaluate the pros and cons, and choose the best course of action. This approach helps build resilience and confidence in handling stressors.
4. Foster a supportive environment:
Creating a supportive environment at home and school is essential for your child’s well-being. Encourage positive relationships, foster a sense of belonging, and teach empathy and kindness. Knowing they have a strong support system can significantly reduce your child’s stress and anxiety levels.
5. Encourage self-care:
Self-care is crucial for both children and adults. Teach your child the importance of taking care of themselves physically, emotionally, and mentally. Encourage activities they enjoy, such as hobbies, spending time in nature, reading, or engaging in creative outlets. These activities provide a much-needed break from stressors and promote overall well-being.
By implementing these strategies, you can support your child in managing stress and anxiety effectively. Remember to lead by example and practice these techniques yourself, as children often learn best through observation. With your guidance and support, your child can develop lifelong skills to navigate the challenges of life with resilience and confidence.
VII. Promoting Healthy Screen Time Habits
In today’s digital age, it is crucial for parents to promote healthy screen time habits for their children. With the increasing use of technology and the internet, setting limits, encouraging educational content, and monitoring online activities are essential for supporting your child’s mental health and overall well-being. In this section, we will explore these strategies in detail.
A. Setting limits on screen time
Setting limits on screen time is an effective way to ensure that your child maintains a healthy balance between online and offline activities. While technology can offer numerous benefits, excessive screen time can have negative effects on your child’s mental health. Here are some tips to help you set appropriate limits:
- Establish clear rules: Create a set of guidelines that outline when and for how long your child can use screens. Be consistent and enforce these rules consistently.
- Lead by example: Show your child that you also limit your own screen time. This will reinforce the importance of balance and moderation.
- Encourage alternative activities: Provide your child with a variety of engaging offline activities, such as sports, arts and crafts, or reading, to divert their attention from screens.
- Use parental control tools: Utilize parental control features on devices and apps to set time limits and restrict access to inappropriate content.
By setting limits on screen time, you can help your child develop healthy habits and reduce the risk of excessive technology use.
B. Encouraging educational and age-appropriate content
While it’s important to limit screen time, it’s equally important to ensure that the time your child spends online is productive and educational. By encouraging educational and age-appropriate content, you can make screen time a valuable learning experience. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Curate a list of trusted websites and apps: Research and identify reputable websites and apps that offer educational content suitable for your child’s age and interests.
- Engage in co-viewing: Watch or explore online content with your child. This allows you to guide their choices, discuss what they are watching, and enhance their understanding.
- Encourage interactive learning: Look for interactive educational games and activities that promote critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity.
- Support their interests: Help your child find online resources related to their hobbies or passions. This can foster a love for learning and encourage them to explore new subjects.
By encouraging educational and age-appropriate content, you can transform screen time into a valuable opportunity for your child’s growth and development.
C. Monitoring online activities and promoting digital safety
In today’s digital landscape, it’s crucial for parents to monitor their child’s online activities and promote digital safety. Here are some steps you can take to ensure your child’s online well-being:
- Establish open communication: Create an environment where your child feels comfortable discussing their online experiences and concerns. Encourage them to come to you if they encounter any issues.
- Teach online safety: Educate your child about the importance of protecting their personal information, avoiding strangers online, and recognizing potential online threats.
- Set privacy settings: Help your child configure privacy settings on social media platforms and other online accounts to limit access to their personal information.
- Regularly review online activities: Monitor your child’s online interactions, including social media usage, messaging apps, and gaming platforms. Be aware of who they are connecting with and what they are sharing.
- Encourage responsible online behavior: Teach your child about the impact of their online actions and the importance of treating others with respect and kindness.
By monitoring online activities and promoting digital safety, you can protect your child from potential online risks and ensure their overall well-being.
Supporting your child’s mental health in the digital age requires a proactive approach. By setting limits on screen time, encouraging educational content, and monitoring online activities, you can create a healthy and safe digital environment for your child to thrive.
VIII. Supporting Your Child’s Emotional Well-being
Supporting your child’s emotional well-being is crucial for their overall mental health. As a parent, you play a vital role in helping your child navigate their emotions and develop healthy coping mechanisms. Here are some strategies to support your child’s emotional well-being:
A. Validating their feelings and emotions
One of the most important ways to support your child’s emotional well-being is by validating their feelings and emotions. It’s essential to let your child know that their emotions are valid and that it’s okay to feel a certain way. Avoid dismissing or minimizing their feelings, as this can make them feel unheard or misunderstood.
Instead, take the time to listen to your child and empathize with their emotions. Reflect back their feelings by saying things like, “I can see that you’re feeling sad/frustrated/angry.” This validation helps your child feel understood and accepted, which is essential for their emotional well-being.
Additionally, encourage open communication with your child. Create a safe space where they feel comfortable expressing their emotions without fear of judgment or punishment. Let them know that it’s okay to talk about their feelings and that you are there to support them.
B. Teaching emotional regulation skills
Emotional regulation is a crucial skill that helps children manage their emotions effectively. By teaching your child how to regulate their emotions, you empower them to navigate challenging situations and cope with stress in a healthy way.
Start by helping your child identify their emotions. Teach them the names of different emotions and help them recognize the physical sensations associated with each emotion. For example, you can say, “When you feel angry, your face might get hot, and your fists might clench.”
Once your child can identify their emotions, teach them strategies for managing those emotions. Deep breathing exercises, counting to ten, or taking a break can all be effective techniques for calming down. Encourage your child to practice these strategies when they are feeling overwhelmed or upset.
Furthermore, model healthy emotional regulation yourself. Children learn by observing their parents, so it’s essential to demonstrate how to handle emotions in a constructive way. Show your child how you cope with stress or frustration, and explain your thought process behind your actions.
C. Encouraging expression through art, writing, or other creative outlets
Art, writing, and other creative outlets can be powerful tools for emotional expression. Encouraging your child to engage in creative activities can help them process their emotions and gain a deeper understanding of themselves.
Provide your child with art supplies, journals, or other materials that allow them to express themselves creatively. Encourage them to draw, paint, write stories, or engage in any other form of creative expression they enjoy.
When your child creates something, take the time to discuss their artwork or writing with them. Ask open-ended questions about their creations, such as, “What inspired you to draw this?” or “How do you feel when you look at this painting?” This dialogue can help your child explore their emotions and gain insights into their inner world.
Additionally, consider engaging in creative activities together as a family. This not only strengthens your bond but also creates a supportive environment where emotional expression is valued.
Remember, supporting your child’s emotional well-being is an ongoing process. Be patient and understanding as they navigate their emotions, and provide a safe and nurturing environment for them to grow.
IX. Identifying and Addressing Bullying
As a parent, it is crucial to be aware of the different types of bullying that your child may encounter. By understanding these types, you can better identify and address any instances of bullying that your child may be experiencing.
A. Understanding the different types of bullying
Bullying can manifest in various forms, and it is essential to recognize each type to effectively address the issue. Here are some common types of bullying:
- Verbal bullying: This type of bullying involves using words to hurt, humiliate, or intimidate the victim. It may include name-calling, teasing, or making derogatory comments.
- Physical bullying: Physical bullying involves any form of physical aggression or harm towards the victim. It can include hitting, pushing, kicking, or damaging personal belongings.
- Relational bullying: Relational bullying focuses on damaging the victim’s social relationships. It may involve spreading rumors, excluding the victim from social activities, or manipulating friendships.
- Cyberbullying: With the rise of technology, cyberbullying has become increasingly prevalent. It occurs through electronic means, such as social media, text messages, or online forums. Cyberbullying can include spreading rumors, sharing embarrassing photos or videos, or sending threatening messages.
By familiarizing yourself with these different types of bullying, you can better identify the signs and take appropriate action to address the issue.
B. Signs that your child may be a victim of bullying
Recognizing the signs that your child may be a victim of bullying is crucial in addressing the issue promptly. While every child may react differently, here are some common signs to look out for:
- Changes in behavior: If your child suddenly becomes withdrawn, anxious, or exhibits changes in mood or behavior, it may be an indication that they are experiencing bullying.
- Physical symptoms: Bullying can often manifest in physical symptoms such as unexplained bruises, cuts, or other injuries.
- Decline in academic performance: If your child’s grades suddenly drop or they show a lack of interest in school, it could be a result of bullying affecting their self-esteem and concentration.
- Social withdrawal: Victims of bullying may isolate themselves from friends and social activities, avoiding situations where they may encounter their bullies.
- Changes in sleep or appetite: Bullying can cause stress and anxiety, leading to changes in sleep patterns or appetite.
It is important to remember that these signs may not definitively indicate bullying, but they should serve as a starting point for further investigation and open communication with your child.
C. Steps to take if your child is being bullied
If you suspect or confirm that your child is being bullied, it is crucial to take immediate action to address the situation. Here are some steps you can take:
- Listen and validate: Start by listening to your child’s experiences and emotions. Provide a safe space for them to express themselves without judgment.
- Document incidents: Keep a record of any incidents of bullying, including dates, times, locations, and descriptions of what occurred. This documentation can be helpful when discussing the issue with school authorities or other relevant parties.
- Contact the school: Reach out to your child’s school to inform them about the bullying and request a meeting with the appropriate staff members. Provide them with the documented incidents and collaborate on a plan to address the issue.
- Encourage resilience: Help your child build resilience by teaching them coping strategies and self-defense techniques. Encourage them to assert themselves and seek support from trusted adults or friends.
- Involve other authorities if necessary: If the bullying persists or escalates despite your efforts, consider involving local authorities or seeking legal advice to ensure your child’s safety and well-being.
Remember, addressing bullying requires a collaborative effort between parents, schools, and the community. By taking proactive steps and supporting your child, you can help them navigate through this challenging experience and ensure their mental health and well-being.
In order to support your child’s mental health, it is crucial to create a supportive school environment. This can be achieved through collaboration with teachers and school staff, promoting anti-bullying policies and programs, and providing resources for mental health support in schools.
Collaboration with Teachers and School Staff
One of the key factors in creating a supportive school environment is collaboration with teachers and school staff. Working together as a team can help identify and address any mental health concerns your child may be facing. Here are some ways to foster collaboration:
- Regular communication: Maintain open lines of communication with your child’s teachers and school staff. This can be done through emails, phone calls, or in-person meetings. Share any concerns or observations you have about your child’s mental health.
- Share resources: Provide teachers and school staff with resources on mental health. This can include articles, books, or websites that offer information and strategies for supporting students’ mental well-being.
- Attend parent-teacher meetings: Take advantage of parent-teacher meetings to discuss your child’s mental health. Share any updates or changes in your child’s behavior or emotional well-being.
- Participate in school activities: Get involved in school activities and events. This can help build relationships with teachers and school staff, fostering a sense of community and support.
Promoting Anti-Bullying Policies and Programs
Bullying can have a significant impact on a child’s mental health. By promoting anti-bullying policies and programs, schools can create a safe and inclusive environment for all students. Here are some ways to promote anti-bullying:
- Educate students: Teach students about the consequences of bullying and the importance of treating others with respect and kindness. Incorporate anti-bullying lessons into the curriculum.
- Implement reporting mechanisms: Establish a system for students to report bullying incidents anonymously. Ensure that all reports are taken seriously and appropriate action is taken.
- Train staff: Provide training for teachers and school staff on how to identify and address bullying. Equip them with strategies to intervene and support students who may be experiencing bullying.
- Encourage bystander intervention: Teach students the importance of standing up against bullying. Encourage them to speak out and support their peers who may be targets of bullying.
Providing Resources for Mental Health Support in Schools
Having resources for mental health support readily available in schools is essential for creating a supportive environment. Here are some ways to provide resources:
- School counseling services: Ensure that the school has qualified counselors who can provide support to students. Counselors can offer individual counseling, group therapy, and crisis intervention.
- Peer support programs: Implement peer support programs where older students can mentor and support younger students. This can create a sense of belonging and provide a safe space for students to discuss their mental health.
- Partnerships with mental health organizations: Collaborate with local mental health organizations to provide workshops, presentations, and resources for students, parents, and school staff.
- Wellness initiatives: Promote wellness initiatives such as mindfulness exercises, yoga classes, or stress management workshops. These activities can help students develop coping skills and promote overall well-being.
By focusing on collaboration with teachers and school staff, promoting anti-bullying policies and programs, and providing resources for mental health support in schools, you can create a supportive school environment that prioritizes your child’s mental well-being.
