Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. Understanding Energy Efficiency in Older Homes
- III. Assessing Energy Efficiency in Your Home
- IV. Improving Insulation in Older Homes
- V. Sealing Air Leaks in Older Homes
- VI. Upgrading Heating and Cooling Systems
- VII. Energy-Efficient Appliances and Lighting
- VIII. Utilizing Renewable Energy Sources
I. Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on how to improve energy efficiency in older homes. If you own an older home, you may have noticed that it tends to be less energy-efficient compared to newer constructions. This can result in higher energy bills and a negative impact on the environment.
In this article, we will explore various strategies and tips that can help you optimize energy usage in your older home. From insulation upgrades to appliance replacements, we will cover everything you need to know to make your home more energy-efficient.
Our target audience for this article includes homeowners with older properties who are looking for practical solutions to reduce their energy consumption. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or prefer hiring professionals, this guide will provide you with actionable steps to improve energy efficiency.
Our goals for this article are to educate readers about the importance of energy efficiency, provide them with a comprehensive understanding of the challenges faced by older homes, and offer practical solutions to address these challenges.
Before we dive into the details, let’s take a moment to analyze the competition. By conducting a competitive analysis, we can identify what other articles are doing well and how we can differentiate ourselves. We aim to create an outline that is more comprehensive, informative, and engaging than existing articles on the same topic.
Throughout this guide, we will support our claims with data and statistics to enhance the credibility and authority of the information provided. We will maintain a consistent tone and style, using a conversational approach to engage readers and keep them interested.
Now that we have set the stage, let’s move on to the next section of our guide, where we will explore the challenges faced by older homes in terms of energy efficiency.
II. Understanding Energy Efficiency in Older Homes
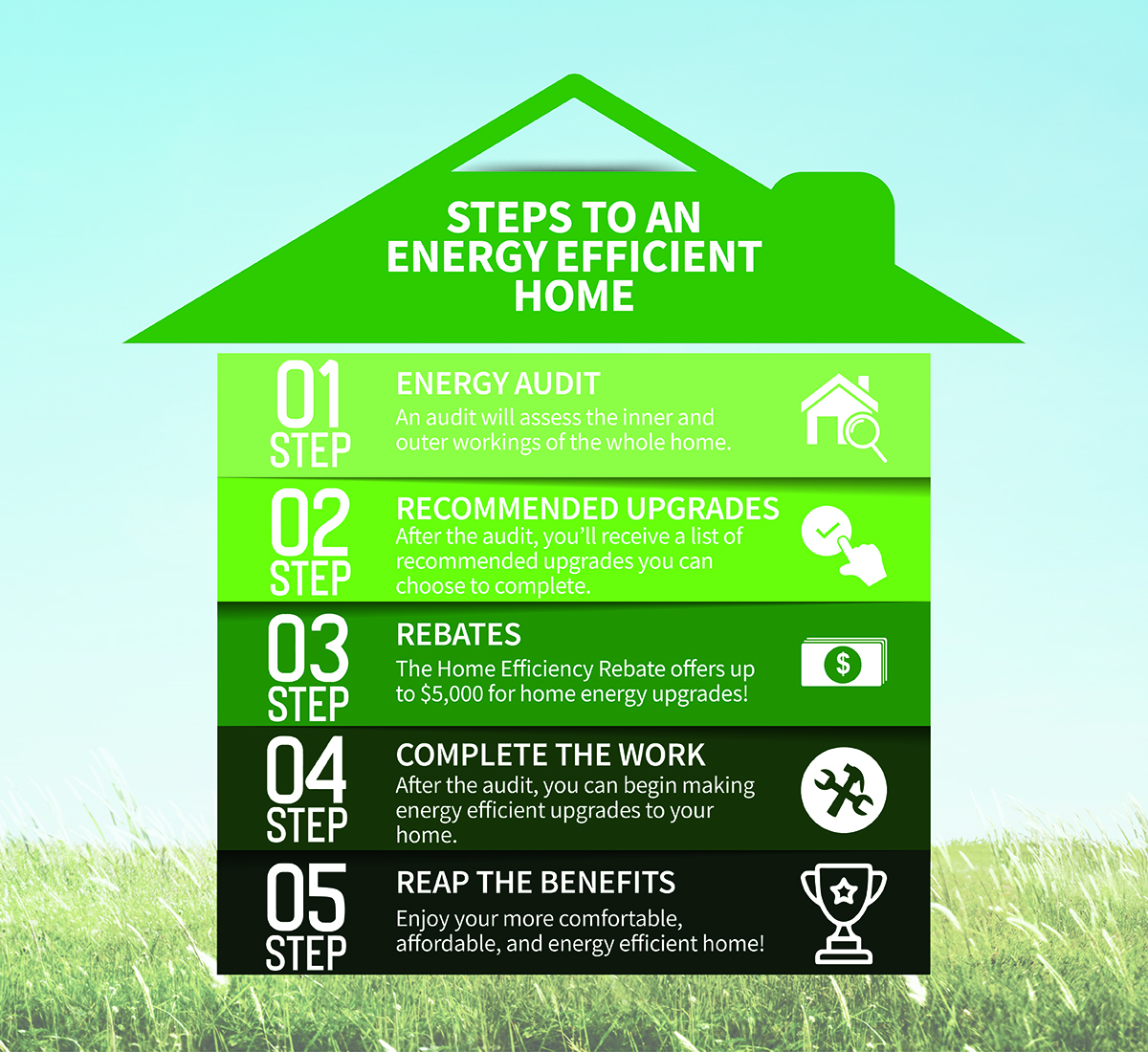
Improving energy efficiency in older homes is a key concern for homeowners looking to reduce their energy consumption and lower their utility bills. However, before we delve into the solutions, it is important to understand the factors contributing to energy inefficiency in these homes and the common issues they face. By identifying these factors and issues, homeowners can take targeted steps to improve the energy efficiency of their older homes.
A. Factors contributing to energy inefficiency
Several factors contribute to the energy inefficiency of older homes. These factors often result from outdated construction practices and materials that were not designed with energy efficiency in mind. Understanding these factors can help homeowners address them effectively.
1. Poor insulation: One of the primary reasons for energy inefficiency in older homes is inadequate insulation. Many older homes were built before modern insulation standards were established, resulting in heat loss during the winter and heat gain during the summer. This lack of insulation leads to increased energy consumption as homeowners rely more on heating and cooling systems to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
2. Drafts and air leaks: Another common issue in older homes is the presence of drafts and air leaks. Over time, gaps and cracks can develop in the walls, windows, doors, and other areas of the home, allowing outside air to enter and conditioned air to escape. These drafts and air leaks not only compromise the comfort of the home but also contribute to higher energy usage as heating and cooling systems work harder to compensate for the loss.
3. Inefficient heating and cooling systems: Older homes often have outdated heating and cooling systems that are less energy-efficient compared to modern systems. These systems may lack proper insulation, have worn-out components, or operate on inefficient fuels. As a result, they consume more energy to provide the same level of comfort as newer, more efficient systems.
4. Outdated appliances and lighting: The appliances and lighting fixtures in older homes are typically less energy-efficient than their modern counterparts. Older refrigerators, dishwashers, washing machines, and other appliances consume more energy to perform the same tasks as newer, energy-efficient models. Similarly, outdated lighting fixtures that use incandescent bulbs consume more energy compared to energy-saving LED bulbs.
B. Common issues in older homes
When it comes to energy efficiency in older homes, several common issues need to be addressed. By identifying and resolving these issues, homeowners can significantly improve the energy efficiency of their homes.
1. Poor insulation
Poor insulation is a prevalent issue in older homes and a major contributor to energy inefficiency. To address this issue, homeowners can consider adding insulation to the walls, attic, and floors. Insulation materials such as fiberglass, cellulose, and spray foam can effectively reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency.
2. Drafts and air leaks
Addressing drafts and air leaks is crucial for improving the energy efficiency of older homes. Homeowners can start by sealing gaps and cracks around windows, doors, and other openings using weatherstripping, caulk, or expanding foam. Installing storm windows and doors can also provide an additional layer of insulation and reduce air leakage.
3. Inefficient heating and cooling systems
Upgrading to a more energy-efficient heating and cooling system is a significant step towards improving energy efficiency in older homes. Homeowners can consider replacing outdated systems with high-efficiency furnaces, boilers, air conditioners, or heat pumps. Regular maintenance and tune-ups are also essential to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
4. Outdated appliances and lighting
Replacing outdated appliances and lighting fixtures with energy-efficient models is an effective way to reduce energy consumption in older homes. Homeowners can choose ENERGY STAR certified appliances that meet strict energy efficiency standards. Switching to LED bulbs for lighting fixtures can also result in significant energy savings.
By addressing these common issues and implementing energy-efficient solutions, homeowners can improve the energy efficiency of their older homes. Not only will this lead to lower energy bills, but it will also contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly lifestyle.
III. Assessing Energy Efficiency in Your Home

Improving energy efficiency in older homes is a crucial step towards reducing energy consumption and lowering utility bills. To effectively assess the energy efficiency of your home, it is important to conduct a thorough home energy audit. This audit will help identify areas of improvement and prioritize energy-saving measures. In this section, we will guide you through the process of conducting a home energy audit and highlight key areas to focus on.
A. Conducting a home energy audit
Conducting a home energy audit is the first step towards assessing the energy efficiency of your home. This process involves a comprehensive evaluation of various aspects of your home’s energy usage. Here are some steps to follow:
- Start by examining your utility bills to understand your energy consumption patterns over time. Look for any significant fluctuations or unusual trends.
- Inspect your home’s insulation to ensure it is properly installed and in good condition. Check for any gaps, cracks, or areas of inadequate insulation.
- Assess your heating and cooling systems, including the furnace, air conditioner, and ductwork. Look for signs of wear and tear, inefficiencies, or outdated equipment.
- Evaluate your appliances and lighting fixtures for energy efficiency. Consider replacing old appliances with energy-efficient models and switching to LED or CFL bulbs.
- Check for air leaks around windows, doors, and other openings. Use weatherstripping, caulking, or other sealing methods to eliminate drafts and reduce energy loss.
B. Identifying areas of improvement
Once you have conducted a home energy audit, it is time to identify specific areas of improvement. Here are some key areas to focus on:
1. Insulation inspection
Proper insulation is essential for maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature and reducing energy waste. Inspect your home’s insulation and address any issues such as gaps, inadequate coverage, or damaged insulation. Consider adding insulation to areas that are poorly insulated, such as attics, basements, and crawl spaces.
2. Checking for air leaks
Air leaks can significantly impact the energy efficiency of your home. Common areas for air leaks include windows, doors, electrical outlets, and plumbing penetrations. Use weatherstripping, caulking, or foam sealants to seal these gaps and prevent air leakage. This will help maintain a consistent indoor temperature and reduce the workload on your heating and cooling systems.
3. Evaluating heating and cooling systems
Heating and cooling systems are major contributors to energy consumption in homes. Evaluate the efficiency of your furnace, air conditioner, and ductwork. Consider upgrading to energy-efficient models or implementing energy-saving features such as programmable thermostats. Regular maintenance and cleaning of these systems can also improve their efficiency.
4. Assessing appliances and lighting
Older appliances and inefficient lighting fixtures can consume a significant amount of energy. Consider replacing outdated appliances with energy-efficient models that have higher Energy Star ratings. Switching to LED or CFL bulbs can also reduce energy consumption and provide longer-lasting lighting solutions.
By following these steps and addressing the identified areas of improvement, you can significantly improve the energy efficiency of your older home. Not only will this help reduce your environmental impact, but it will also lead to long-term cost savings on your energy bills.
IV. Improving Insulation in Older Homes

Improving insulation in older homes is essential for increasing energy efficiency and reducing utility costs. Older homes often lack proper insulation, leading to heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer. In this section, we will explore different types of insulation materials and methods for insulating the attic, walls, floors, and sealing gaps and cracks.
A. Types of insulation materials
When it comes to improving insulation in older homes, choosing the right insulation material is crucial. Here are some commonly used insulation materials:
- Fiberglass insulation: Fiberglass insulation is made of tiny glass fibers and is one of the most popular insulation materials. It comes in batts or rolls and is relatively easy to install.
- Spray foam insulation: Spray foam insulation is a versatile option that expands to fill gaps and cracks. It provides excellent insulation and helps to create an airtight seal.
- Cellulose insulation: Cellulose insulation is made from recycled paper and treated with fire retardants. It is an eco-friendly option and can be blown into attics and walls.
- Rigid foam insulation: Rigid foam insulation is a durable and moisture-resistant material. It is commonly used for insulating foundations, basements, and exterior walls.
Each insulation material has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to consider factors such as cost, R-value, and ease of installation when choosing the right material for your home.
B. Insulating the attic
The attic is one of the primary areas where heat loss and gain occur in older homes. Properly insulating the attic can significantly improve energy efficiency. Here are some steps to insulate the attic:
- Seal air leaks: Before adding insulation, it’s important to seal any air leaks in the attic. Use caulk or weatherstripping to seal gaps around windows, doors, and vents.
- Add insulation: Depending on the type of insulation material chosen, install insulation between the attic floor joists or over the existing insulation. Ensure that the insulation is evenly distributed and covers the entire attic space.
- Provide ventilation: Proper attic ventilation is essential to prevent moisture buildup and maintain a healthy indoor environment. Install soffit vents and ridge vents to promote airflow.
By insulating the attic, you can create a thermal barrier that prevents heat transfer between the living space and the outside environment.
C. Insulating walls and floors
Insulating walls and floors is another crucial step in improving energy efficiency in older homes. Here’s how you can insulate walls and floors:
- Wall insulation: If your home has accessible walls, you can install insulation by drilling holes and blowing in loose-fill insulation or inserting batts through the holes. Alternatively, you can consider adding insulation to the exterior walls during a renovation.
- Floor insulation: Insulating floors can help prevent heat loss and make your home more comfortable. Depending on the type of flooring, you can install insulation between floor joists or use rigid foam insulation panels.
Properly insulating walls and floors can reduce drafts, improve comfort, and lower heating and cooling costs.
D. Sealing gaps and cracks
Gaps and cracks in the building envelope can significantly impact energy efficiency. Here are some tips for sealing gaps and cracks in older homes:
- Inspect for air leaks: Conduct a thorough inspection of your home to identify areas with gaps and cracks. Common areas include windows, doors, electrical outlets, and plumbing penetrations.
- Use weatherstripping: Apply weatherstripping around windows and doors to create a tight seal. Choose weatherstripping materials that are suitable for the specific application.
- Apply caulk or foam sealant: Use caulk or foam sealant to seal gaps and cracks in walls, floors, and ceilings. Ensure that the sealant is compatible with the material and provides an airtight seal.
Sealing gaps and cracks can prevent air leakage, improve indoor air quality, and enhance energy efficiency in older homes.
Improving insulation in older homes is a worthwhile investment that can lead to long-term energy savings and increased comfort. By choosing the right insulation materials, insulating the attic, walls, and floors, and sealing gaps and cracks, you can significantly improve the energy efficiency of your home. Take the necessary steps to enhance insulation and enjoy the benefits of a more energy-efficient and comfortable living space.
V. Sealing Air Leaks in Older Homes
As an experienced contractor specializing in energy efficiency, I have come across numerous older homes that suffer from air leaks. These leaks can significantly impact the energy efficiency of a home, leading to higher energy bills and a less comfortable living environment. In this section, I will discuss common air leak locations in older homes and provide techniques for caulking, weatherstripping, sealing windows and doors, and insulating ductwork to improve energy efficiency.
A. Identifying common air leak locations
Before you can effectively seal air leaks in your older home, it’s important to identify the common areas where these leaks occur. Here are some key areas to check:
- Windows and doors: Check for gaps and cracks around the frames, as well as worn-out weatherstripping.
- Electrical outlets and switch plates: These can be major sources of air leaks, especially if they are located on exterior walls.
- Pipes and plumbing penetrations: Look for gaps around pipes that enter or exit your home.
- Attic access points: Make sure the access hatch or door is properly sealed to prevent air leakage.
- Baseboards and crown molding: Inspect these areas for gaps or cracks where air could escape.
By thoroughly inspecting these areas, you can pinpoint the specific locations where air leaks are occurring and prioritize your sealing efforts.
B. Caulking and weatherstripping techniques
Caulking and weatherstripping are two effective techniques for sealing air leaks in older homes. Here’s how to do it:
- Caulking: Use a high-quality caulk to seal gaps and cracks around windows, doors, and other areas where air is escaping. Apply the caulk in a continuous bead, ensuring full coverage of the gap. Smooth the caulk with a caulk finishing tool or your finger for a neat finish.
- Weatherstripping: Replace worn-out weatherstripping around windows and doors to create a tight seal. Choose weatherstripping materials that are appropriate for your specific needs, such as adhesive-backed foam tape or V-strip weatherstripping. Measure and cut the weatherstripping to fit the dimensions of the window or door, then apply it to create a seal.
These techniques may require some time and effort, but they can significantly reduce air leakage in your home and improve energy efficiency.
C. Sealing windows and doors
Windows and doors are common culprits for air leaks in older homes. Here are some additional tips for effectively sealing them:
- Window film: Apply window film to single-pane windows to improve insulation and reduce drafts. Window film is easy to install and can make a noticeable difference in energy efficiency.
- Door sweeps: Install door sweeps on exterior doors to seal the gap between the door and the floor. This will prevent cold drafts from entering your home.
- Storm windows and doors: Consider installing storm windows and doors for added insulation and protection against air leaks. These can be particularly beneficial for older homes with single-pane windows.
By taking these additional steps to seal windows and doors, you can further enhance the energy efficiency of your older home.
D. Insulating ductwork
Insulating ductwork is another important aspect of improving energy efficiency in older homes. Here’s what you need to know:
- Inspect ductwork: Start by inspecting the ductwork in your home for any visible gaps, loose connections, or damaged insulation. These issues can contribute to air leaks and reduce the effectiveness of your HVAC system.
- Seal gaps and connections: Use duct sealant or metal tape to seal any gaps or loose connections in the ductwork. Make sure to clean the surfaces before applying the sealant or tape for better adhesion.
- Insulate ducts: If your ductwork is located in unconditioned areas such as the attic or crawl space, consider insulating it to prevent heat loss or gain. Use insulation materials specifically designed for ductwork, such as duct insulation sleeves or wraps.
Properly sealed and insulated ductwork can improve the efficiency of your heating and cooling system, resulting in energy savings and a more comfortable home.
By following these techniques for sealing air leaks in older homes, you can significantly improve energy efficiency, reduce energy bills, and create a more comfortable living environment. Take the time to identify and address air leaks in your home, and enjoy the benefits of a more energy-efficient living space.
VI. Upgrading Heating and Cooling Systems
When it comes to improving energy efficiency in older homes, upgrading heating and cooling systems is a crucial step. The efficiency of existing systems should be evaluated to determine if they need to be replaced or upgraded. Here are some key considerations and options to explore:
A. Evaluating the efficiency of existing systems
Before making any decisions, it’s important to assess the efficiency of your current heating and cooling systems. This can be done by conducting an energy audit or seeking professional advice. An energy audit will help identify any areas where your systems may be wasting energy and provide recommendations for improvement.
During the evaluation process, factors such as the age of the systems, their maintenance history, and their overall performance should be taken into account. Older systems tend to be less efficient and may require more frequent repairs, making them good candidates for replacement.
B. Replacing or upgrading furnaces and boilers
If your existing furnace or boiler is outdated and inefficient, it may be time to consider a replacement. Newer models are designed to be more energy-efficient, resulting in lower utility bills and reduced environmental impact.
When choosing a new furnace or boiler, look for models with high Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) ratings. AFUE measures the efficiency of the system in converting fuel into heat. The higher the AFUE rating, the more efficient the system is. Aim for a rating of 90% or higher for optimal energy savings.
In addition to replacing the entire system, upgrading specific components can also improve efficiency. For example, installing a variable-speed blower motor can help reduce energy consumption by adjusting the airflow to match the heating or cooling demands of your home.
C. Installing energy-efficient air conditioning units
Older air conditioning units can be major energy guzzlers, especially if they are not properly maintained or are nearing the end of their lifespan. Upgrading to energy-efficient models can significantly reduce your cooling costs while keeping your home comfortable.
Look for air conditioning units with a high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) rating. SEER measures the cooling output of the system divided by the energy it consumes. The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the unit is. Aim for a rating of 16 or higher for optimal energy savings.
In addition to the SEER rating, consider other features such as programmable thermostats, which allow you to set specific temperature schedules and reduce energy usage when you’re away from home.
D. Utilizing programmable thermostats
Programmable thermostats are an excellent tool for improving energy efficiency in older homes. These devices allow you to set different temperature settings for different times of the day, ensuring that your heating and cooling systems are only running when needed.
By programming your thermostat to lower the temperature during times when you’re away or asleep, you can save energy and reduce your utility bills. Some advanced models even have Wi-Fi connectivity, allowing you to control the thermostat remotely using your smartphone or other smart devices.
When choosing a programmable thermostat, opt for models that are compatible with your existing heating and cooling systems. Consider features such as zoning capabilities, which allow you to control the temperature in different areas of your home independently.
VII. Energy-Efficient Appliances and Lighting
In today’s world, where energy conservation is of utmost importance, it is essential to make conscious choices when it comes to appliances and lighting in our homes. By opting for energy-efficient appliances and utilizing smart lighting solutions, we can significantly reduce our energy consumption and contribute to a greener environment. In this section, we will explore various ways to improve energy efficiency in older homes by choosing energy-efficient appliances, upgrading to LED lighting, using smart power strips, and incorporating natural lighting.
A. Choosing Energy-Efficient Appliances
When it comes to selecting appliances for your home, it is crucial to consider their energy efficiency ratings. Look for appliances that are ENERGY STAR certified, as they meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). These appliances are designed to consume less energy without compromising on performance.
Consider the size and capacity of the appliances you choose. Opt for smaller models if they meet your needs, as larger appliances tend to consume more energy. Additionally, look for appliances with advanced features such as energy-saving modes, programmable settings, and sensors that automatically adjust power usage based on usage patterns.
It is also worth noting that certain appliances consume more energy than others. For example, refrigerators, air conditioners, and water heaters are typically the biggest energy consumers in a household. Therefore, it is advisable to invest in energy-efficient models for these appliances to maximize energy savings.
B. Upgrading to LED Lighting
One of the most effective ways to improve energy efficiency in older homes is by upgrading to LED lighting. LED (Light Emitting Diode) bulbs are highly energy-efficient and have a significantly longer lifespan compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. They consume up to 80% less energy and can last up to 25 times longer.
LED bulbs are available in various color temperatures and brightness levels, making it easy to find the perfect lighting for every room in your home. They also emit less heat, reducing the strain on your cooling systems during hot summer months.
Consider replacing all your existing incandescent and CFL bulbs with LED bulbs. Start with frequently used areas such as the kitchen, living room, and bedrooms. Gradually replace bulbs in other areas of your home to maximize energy savings.
C. Using Smart Power Strips
Smart power strips are a convenient and effective way to reduce energy wastage caused by standby power. Standby power, also known as vampire power, refers to the energy consumed by electronic devices even when they are turned off or in standby mode.
Smart power strips work by cutting off power supply to devices that are not in use. They often come with built-in timers, motion sensors, or remote controls, allowing you to easily control power usage. By using smart power strips, you can eliminate standby power consumption and reduce your energy bills.
Place smart power strips in areas where you have multiple devices connected, such as entertainment centers, home offices, and kitchens. This way, you can easily turn off all devices with a single switch or through a mobile app.
D. Incorporating Natural Lighting
Maximizing natural lighting in your home is not only energy-efficient but also enhances the overall ambiance and aesthetics. By allowing natural light to enter your home, you can reduce the need for artificial lighting during the day.
Start by cleaning your windows regularly to ensure maximum light transmission. Consider using sheer curtains or blinds that allow light to pass through while maintaining privacy. Position mirrors strategically to reflect natural light and brighten up darker areas of your home.
If possible, consider adding skylights or light tubes to areas that lack natural light, such as hallways or bathrooms. These additions can bring in ample daylight, reducing the need for artificial lighting during daylight hours.
Additionally, consider landscaping options that allow natural light to enter your home. Trim trees or shrubs that obstruct sunlight from reaching windows, and strategically place plants near windows to create a pleasant green view while still allowing light to enter.
By implementing these energy-efficient practices, you can significantly improve energy efficiency in older homes. Not only will you reduce your carbon footprint, but you will also enjoy long-term energy savings and a more comfortable living environment.
VIII. Utilizing Renewable Energy Sources
In today’s world, where environmental concerns are at the forefront of our minds, finding ways to reduce our carbon footprint and decrease our reliance on non-renewable energy sources is crucial. Thankfully, there are several renewable energy options available that can be easily implemented in older homes. In this section, we will explore three popular methods of utilizing renewable energy sources: installing solar panels, harnessing geothermal energy, and exploring wind energy options.
A. Installing Solar Panels
Solar panels have become increasingly popular in recent years as a way to harness the power of the sun and convert it into usable energy. Installing solar panels on the roof of an older home can provide a significant reduction in energy costs and contribute to a more sustainable lifestyle.
When considering installing solar panels, it is important to assess the suitability of your home’s roof. Ideally, the roof should have a south-facing aspect with minimal shading from trees or neighboring buildings. Additionally, the roof should be structurally sound enough to support the weight of the solar panels.
Once the suitability of the roof has been determined, it is advisable to consult with a professional solar panel installation company. They will be able to assess your energy needs, design a system that is tailored to your home, and handle the installation process. Additionally, they can guide you through any necessary permits or paperwork required for connecting your solar panels to the grid.
By installing solar panels, you can take advantage of the sun’s abundant energy and reduce your reliance on traditional energy sources. Not only will this help the environment, but it can also lead to long-term cost savings on your energy bills.
B. Harnessing Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is another renewable energy source that can be utilized in older homes. This method harnesses the natural heat stored beneath the Earth’s surface to provide heating and cooling for your home.
One of the main advantages of geothermal energy is its consistency. Unlike solar or wind energy, which can be intermittent depending on weather conditions, geothermal energy is available year-round. This makes it a reliable and efficient option for heating and cooling your home.
To harness geothermal energy, a geothermal heat pump system is installed. This system consists of a series of pipes buried in the ground, which circulate a fluid that absorbs heat from the Earth and transfers it to your home. In the winter, the system extracts heat from the ground and distributes it throughout your home, providing warmth. In the summer, the process is reversed, and the system removes heat from your home, providing cooling.
Installing a geothermal heat pump system requires careful planning and professional expertise. The system needs to be properly sized to meet the heating and cooling demands of your home. Additionally, the ground conditions and available space for the installation need to be assessed. Consulting with a geothermal energy specialist will ensure that the system is designed and installed correctly.
By harnessing geothermal energy, you can significantly reduce your reliance on traditional heating and cooling methods, leading to both environmental and cost-saving benefits.
C. Exploring Wind Energy Options
Wind energy is a renewable energy source that has been utilized for centuries. While it may not be as feasible for every older home, it is worth exploring the potential for harnessing wind energy in your area.
Before considering wind energy options, it is important to assess the wind resources in your location. Wind turbines require a consistent and sufficient wind speed to generate electricity effectively. Conducting a wind resource assessment or consulting with a wind energy professional can help determine the viability of wind energy for your home.
If your location is suitable for wind energy, there are two main options to consider: small-scale wind turbines and community wind projects. Small-scale wind turbines are typically installed on the property and can provide electricity for individual homes. Community wind projects involve multiple turbines installed in a shared location, with the generated electricity distributed to multiple homes or businesses.
When considering wind energy options, it is important to be aware of any local regulations or restrictions that may apply. Some areas have height restrictions or zoning requirements that need to be taken into account when installing wind turbines.
While wind energy may not be suitable for every older home, it is worth exploring the potential benefits in terms of reducing reliance on traditional energy sources and contributing to a more sustainable future.

