Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. Physical Health Benefits of Regular Exercise
- C. Strength and Muscle Tone
- D. Bone Health
- E. Improved Immune Function
- F. Increased Energy Levels
- III. Mental Health Benefits of Regular Exercise
- C. Cognitive Function
- D. Better Sleep
- IV. Longevity and Disease Prevention
- V. Social and Emotional Benefits of Regular Exercise
I. Introduction

Regular exercise is not just about staying fit or losing weight; it offers a wide range of health benefits that can improve your overall well-being. Engaging in physical activity on a consistent basis can have a positive impact on your physical, mental, and emotional health. Whether you prefer going for a run, hitting the gym, or practicing yoga, incorporating exercise into your daily routine can lead to a healthier and happier life.
In this article, we will explore the top health benefits of regular exercise and why it is important to prioritize physical activity in your lifestyle. From boosting cardiovascular health to enhancing cognitive function, exercise has the power to transform your body and mind.
Exercise is not limited to intense workouts or spending hours at the gym. It can be as simple as taking a brisk walk, dancing, or playing a sport. The key is to find an activity that you enjoy and can sustain in the long term. By making exercise a regular part of your routine, you can reap the numerous benefits it has to offer.
Throughout this article, we will delve into the specific benefits of exercise, backed by scientific research and studies. Whether you are looking to improve your physical fitness, manage stress, or prevent chronic diseases, this article will provide you with valuable insights and practical tips to help you make exercise a priority in your life.
II. Physical Health Benefits of Regular Exercise

A. Weight Management
Regular exercise plays a crucial role in weight management. It helps in weight loss and maintaining a healthy weight in various ways.
1. How exercise helps in weight loss
When you engage in physical activities such as cardio exercises, strength training, or high-intensity interval training (HIIT), your body burns calories. This calorie burn leads to weight loss as it creates a calorie deficit, meaning you are burning more calories than you consume.
Exercise also helps to increase your metabolic rate, which is the rate at which your body burns calories at rest. This means that even after you finish your workout, your body continues to burn calories at an elevated rate.
Furthermore, exercise helps to build lean muscle mass. Muscles are more metabolically active than fat, which means they burn more calories even when you are not exercising. By increasing your muscle mass through exercise, you can boost your metabolism and burn more calories throughout the day.
2. The role of exercise in maintaining a healthy weight
Regular exercise is not only important for weight loss but also for maintaining a healthy weight. It helps to prevent weight gain by balancing the calories you consume with the calories you burn.
Exercise also helps to regulate appetite and control cravings. It can reduce hunger hormones and increase the production of hormones that make you feel full, leading to better portion control and healthier food choices.
Additionally, exercise can improve your body composition by reducing body fat and increasing muscle mass. This can result in a leaner and more toned physique, which is often associated with a healthy weight.
B. Cardiovascular Health
Regular exercise has numerous benefits for cardiovascular health. It can improve heart health and reduce the risk of heart diseases.
1. How exercise improves heart health
Engaging in cardiovascular exercises such as running, cycling, swimming, or brisk walking can strengthen your heart muscle. Regular aerobic exercise helps to increase the efficiency of your heart, allowing it to pump blood more effectively.
Exercise also helps to lower blood pressure and reduce the levels of bad cholesterol (LDL) in your blood. It can increase the levels of good cholesterol (HDL), which helps to remove bad cholesterol from your arteries and reduce the risk of heart diseases.
Furthermore, exercise promotes better blood circulation and improves the health of your blood vessels. It can prevent the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can lead to blockages and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
2. Benefits of regular exercise for reducing the risk of heart diseases
Regular exercise has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of developing heart diseases. It can lower the risk of conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and strokes.
Exercise helps to maintain a healthy weight, control blood pressure, and manage cholesterol levels, all of which are important factors in preventing heart diseases.
Additionally, exercise can improve overall cardiovascular fitness, making your heart and lungs more efficient. This can increase your stamina and endurance, allowing you to engage in daily activities with ease and reduce the risk of heart-related complications.
C. Strength and Muscle Tone
When it comes to exercise, building strength and muscle tone is one of the key goals for many individuals. Not only does it improve physical appearance, but it also has numerous health benefits. In this section, we will explore how exercise helps in building strength and muscle tone, as well as the importance of resistance training in exercise routines.
1. How exercise helps in building strength and muscle tone
Regular exercise plays a crucial role in building strength and muscle tone. When we engage in physical activity, our muscles are put under stress, which causes microscopic damage to the muscle fibers. In response to this damage, our bodies initiate a repair process, where the damaged muscle fibers are rebuilt and strengthened. This process is known as muscle hypertrophy.
Strength training exercises, such as weightlifting, resistance band workouts, and bodyweight exercises, are particularly effective in promoting muscle hypertrophy. These exercises involve the use of external resistance, which forces our muscles to work harder and adapt to the increased demand. Over time, this leads to an increase in muscle size, strength, and tone.
Additionally, exercise stimulates the release of hormones, such as testosterone and growth hormone, which further contribute to muscle growth and development. These hormones help optimize protein synthesis, the process by which our bodies build new muscle tissue.
It is important to note that building strength and muscle tone requires consistency and progressive overload. Consistency refers to regularly engaging in exercise, while progressive overload involves gradually increasing the intensity, duration, or resistance of your workouts. By progressively challenging your muscles, you stimulate further growth and adaptation.
2. The importance of resistance training in exercise routines
Resistance training, also known as strength training or weightlifting, is a vital component of any exercise routine aimed at building strength and muscle tone. This form of exercise involves the use of external resistance, such as dumbbells, barbells, resistance bands, or even your body weight, to challenge your muscles.
One of the primary benefits of resistance training is its ability to target specific muscle groups. By performing exercises that isolate and engage specific muscles, you can effectively strengthen and tone those areas. For example, bicep curls target the biceps, while squats target the quadriceps and glutes.
In addition to targeting specific muscles, resistance training also improves overall muscle coordination and stability. It activates multiple muscle groups simultaneously, promoting better balance and control during movement. This can be particularly beneficial in preventing injuries and improving performance in sports and other physical activities.
Furthermore, resistance training increases bone density and reduces the risk of osteoporosis, especially in older adults. The stress placed on the bones during weightlifting stimulates bone remodeling, leading to stronger and denser bones.
Resistance training also offers numerous metabolic benefits. It increases muscle mass, which in turn boosts metabolism and helps burn more calories even at rest. This can be advantageous for individuals looking to lose weight or maintain a healthy body composition.
It is important to note that resistance training should be performed with proper form and technique to minimize the risk of injury. If you are new to strength training, it is advisable to seek guidance from a qualified fitness professional to ensure you are using correct form and progressing safely.
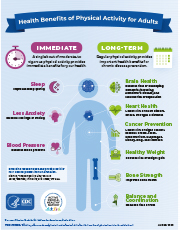
D. Bone Health

When it comes to maintaining strong and healthy bones, exercise plays a crucial role. Regular physical activity has a positive impact on bone density, which is essential for preventing osteoporosis and fractures. By engaging in weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, running, and weightlifting, individuals can stimulate bone growth and increase bone mineral density.
1. The impact of exercise on bone density
Exercise has a direct impact on bone density by stimulating the production of new bone tissue. When we engage in weight-bearing activities, our bones experience stress and strain, which triggers the body to strengthen the bones to better handle the load. This process, known as bone remodeling, helps to increase bone density and improve overall bone health.
Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking or dancing, are particularly effective in promoting bone density. These activities involve supporting our body weight against gravity, which puts stress on the bones and stimulates bone growth. Additionally, resistance training exercises, like weightlifting, can also have a positive impact on bone density by increasing muscle strength and promoting bone health.
2. Exercise recommendations for improving bone health
To improve bone health, it is recommended to engage in weight-bearing exercises for at least 150 minutes per week. This can be achieved through activities such as brisk walking, jogging, dancing, or playing tennis. It is important to choose activities that you enjoy and that fit your fitness level.
In addition to weight-bearing exercises, incorporating resistance training into your routine can further enhance bone health. This can involve using weights, resistance bands, or bodyweight exercises to strengthen the muscles and bones. Aim to include resistance training at least two days a week, targeting all major muscle groups.
E. Improved Immune Function
Regular exercise not only benefits our physical health but also has a positive impact on our immune system. Exercise can help to strengthen our immune response, making us more resilient to infections and diseases.
1. The relationship between exercise and the immune system
Exercise has been shown to have a profound effect on the immune system. When we engage in physical activity, our body undergoes various changes that can enhance immune function. Exercise increases blood circulation, which allows immune cells to move more freely throughout the body. This enables the immune system to detect and eliminate pathogens more efficiently.
Furthermore, exercise has been found to reduce the levels of stress hormones in the body, such as cortisol. High levels of stress hormones can suppress the immune system, making us more susceptible to infections. By reducing stress hormone levels, exercise helps to maintain a balanced immune response.
2. How regular exercise boosts immune function
Regular exercise has been shown to have several positive effects on immune function. It can increase the production of antibodies and enhance the activity of natural killer cells, which are responsible for fighting off viruses and cancer cells. Exercise also improves the circulation of immune cells, allowing them to reach potential infection sites more quickly.
In addition, exercise has been found to reduce inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation can weaken the immune system and contribute to the development of various diseases. By reducing inflammation, exercise helps to maintain a healthy immune system and protect against chronic conditions.
F. Increased Energy Levels
Feeling tired and fatigued can significantly impact our daily lives. However, regular exercise can help to boost energy levels and combat fatigue, allowing us to feel more energized and productive throughout the day.
1. How exercise enhances energy levels
Exercise has a direct impact on our energy levels by increasing blood flow and oxygen delivery to the muscles and tissues. When we engage in physical activity, our heart rate and breathing rate increase, supplying more oxygen and nutrients to the body. This results in improved energy production and a reduction in feelings of fatigue.
Regular exercise also stimulates the release of endorphins, which are natural chemicals in the body that promote feelings of happiness and well-being. These endorphins act as natural energy boosters, improving mood and reducing fatigue.
2. The role of exercise in reducing fatigue
Exercise has been shown to be an effective tool in reducing fatigue and increasing overall energy levels. Even a short bout of exercise, such as a brisk walk or a quick workout, can provide an immediate energy boost. Regular physical activity can also improve sleep quality, which is essential for maintaining energy levels throughout the day.
By incorporating exercise into our daily routine, we can experience long-term benefits in terms of increased energy levels and reduced fatigue. It is recommended to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week to reap the energy-boosting benefits of exercise.
III. Mental Health Benefits of Regular Exercise
A. Stress Reduction
Regular exercise has been proven to be an effective tool in managing stress. When we engage in physical activity, our bodies release endorphins, which are known as the “feel-good” hormones. These endorphins help to reduce stress levels and promote a sense of well-being. Exercise also helps to increase the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which play a crucial role in regulating mood and reducing anxiety.
1. How exercise helps in managing stress
Exercise helps to combat stress in several ways. Firstly, it acts as a distraction from the daily pressures and worries that can contribute to stress. When we focus on our physical activity, we shift our attention away from our problems and allow ourselves to relax and unwind. Additionally, exercise promotes the release of endorphins, which act as natural stress relievers. These endorphins help to improve our mood and reduce feelings of anxiety and tension.
2. The impact of exercise on stress hormones
Regular exercise has a positive impact on stress hormones in our bodies. When we engage in physical activity, our adrenal glands release cortisol, which is known as the stress hormone. However, with regular exercise, our bodies become more efficient at regulating cortisol levels, resulting in a decrease in stress. Exercise also helps to increase the production of endorphins, which counteract the effects of cortisol and promote a sense of calm and relaxation.
B. Mood Enhancement
Exercise has a profound effect on our mood and can significantly improve our overall emotional well-being. When we engage in physical activity, our bodies release endorphins, which are responsible for the feelings of happiness and euphoria commonly known as the “runner’s high.” These endorphins help to boost our mood and provide a natural sense of well-being.
1. The connection between exercise and mood improvement
There is a strong connection between exercise and mood improvement. When we exercise, our bodies release endorphins, which interact with receptors in our brain to reduce pain and increase feelings of pleasure. These endorphins not only help to improve our mood but also provide a sense of accomplishment and self-confidence. Regular exercise has been shown to be an effective treatment for mild to moderate depression, as it helps to alleviate symptoms and improve overall mental well-being.
2. The role of exercise in reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety
Exercise plays a crucial role in reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety. Physical activity helps to increase the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are responsible for regulating mood and promoting feelings of happiness. Regular exercise has been shown to be as effective as medication in treating mild to moderate depression and anxiety. Additionally, exercise provides a healthy coping mechanism for stress and helps to reduce the risk of developing mental health disorders.
C. Cognitive Function
Regular exercise has numerous benefits for cognitive function, including improved memory and concentration. In this section, we will explore how exercise positively impacts cognitive abilities and why it is essential for maintaining a healthy brain.
1. How exercise improves cognitive function
Exercise has been shown to have a profound impact on cognitive function. When we engage in physical activity, our bodies release endorphins, which are natural mood enhancers. These endorphins not only make us feel good but also improve our cognitive abilities.
Physical exercise increases blood flow to the brain, delivering oxygen and nutrients that are essential for optimal brain function. It also promotes the growth of new neurons, particularly in the hippocampus, which is the region of the brain responsible for memory and learning.
Furthermore, exercise stimulates the release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that plays a crucial role in promoting the survival and growth of neurons. BDNF also enhances synaptic plasticity, which is the ability of the brain to adapt and change in response to new experiences.
Studies have consistently shown that individuals who engage in regular exercise have better cognitive function compared to those who lead sedentary lifestyles. Exercise has been found to improve attention, information processing speed, and executive functions such as decision-making and problem-solving.
2. The benefits of exercise for memory and concentration
Exercise has a direct impact on memory and concentration. Research has demonstrated that aerobic exercise, such as running or swimming, can enhance memory and improve cognitive performance.
When we exercise, our bodies release a hormone called cortisol, which helps regulate stress. Elevated levels of cortisol can impair memory and cognitive function. However, regular physical activity has been shown to reduce cortisol levels, leading to improved memory and concentration.
Exercise also increases the production of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, which play a crucial role in regulating mood and cognitive function. These neurotransmitters help improve focus, attention, and overall cognitive performance.
Moreover, exercise promotes neurogenesis, the formation of new neurons in the brain. This process is particularly important for memory and learning. By engaging in regular exercise, we can enhance our brain’s ability to create and retrieve memories.
Additionally, exercise has been found to reduce the risk of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. It can help preserve brain volume and maintain cognitive function as we age.
D. Better Sleep
Getting a good night’s sleep is essential for overall health and well-being. It allows our bodies to rest and recover, and it plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal cognitive function, mood, and physical performance. However, many people struggle with sleep-related issues, such as insomnia or poor sleep quality. The good news is that regular exercise can significantly improve sleep patterns and promote better sleep. In this section, we will explore the relationship between exercise and quality sleep and discuss how exercise can help improve sleep patterns.
1. The relationship between exercise and quality sleep
Exercise has been shown to have a positive impact on sleep quality and duration. Numerous studies have found that individuals who engage in regular physical activity tend to experience better sleep compared to those who are sedentary. The exact mechanisms behind this relationship are not fully understood, but researchers believe that exercise helps regulate our internal body clock, known as the circadian rhythm, which plays a crucial role in sleep-wake cycles.
Exercise also helps reduce anxiety and stress, two common factors that can interfere with sleep. Physical activity stimulates the production of endorphins, also known as “feel-good” hormones, which promote relaxation and improve mood. By reducing anxiety and stress levels, exercise can help individuals fall asleep faster and enjoy a more restful sleep throughout the night.
Additionally, exercise has been found to increase the amount of deep sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep, that individuals experience. Deep sleep is the most restorative stage of sleep, during which the body repairs and rejuvenates itself. By promoting deep sleep, exercise can enhance the overall quality of sleep and leave individuals feeling more refreshed and energized upon waking.
2. How exercise promotes better sleep patterns
Regular exercise can help regulate our sleep-wake cycle and promote better sleep patterns in several ways:
- Increased exposure to natural light: Exercise often takes place outdoors or in well-lit environments, which exposes individuals to natural light. Natural light helps regulate the production of melatonin, a hormone that plays a crucial role in sleep. By increasing exposure to natural light, exercise can help synchronize our internal body clock and improve sleep quality.
- Energy expenditure: Exercise helps burn excess energy and promotes physical fatigue. When we expend energy through exercise, our bodies naturally crave rest and recovery, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night.
- Improved mood and mental well-being: Regular exercise has been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, both of which can negatively impact sleep. By improving mood and mental well-being, exercise can help individuals relax and unwind, leading to better sleep quality.
- Regulation of body temperature: Exercise increases body temperature, and the subsequent drop in temperature after exercise can signal to the body that it’s time to sleep. This drop in temperature helps facilitate the onset of sleep and promotes deeper, more restful sleep.
It’s important to note that the timing of exercise can also impact sleep quality. While any form of physical activity is beneficial, engaging in vigorous exercise too close to bedtime may have a stimulating effect on the body, making it harder to fall asleep. It’s generally recommended to finish exercising at least a few hours before bedtime to allow the body to wind down and prepare for sleep.
IV. Longevity and Disease Prevention
A. Increased Lifespan
Regular exercise has been linked to an increased lifespan, allowing individuals to live longer and healthier lives. Engaging in physical activity on a regular basis has numerous benefits for overall health and longevity.
1. The link between regular exercise and increased lifespan
Research has consistently shown that individuals who engage in regular exercise tend to live longer than those who lead sedentary lifestyles. Physical activity helps to improve cardiovascular health, strengthen the immune system, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases, all of which contribute to a longer lifespan.
2. Exercise recommendations for longevity
In order to reap the benefits of increased lifespan, it is recommended to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week. Additionally, strength training exercises should be incorporated at least two days a week to maintain muscle mass and bone density.
B. Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
Regular exercise plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of chronic diseases. By incorporating physical activity into one’s daily routine, individuals can significantly lower their chances of developing various health conditions.
1. How exercise lowers the risk of chronic diseases
Exercise helps to regulate blood pressure, improve blood sugar control, and reduce inflammation, all of which are key factors in preventing chronic diseases. Physical activity also helps to maintain a healthy weight, which further reduces the risk of developing conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer.
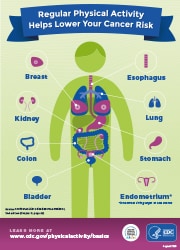
2. The impact of exercise on specific diseases such as diabetes, cancer, and hypertension
Regular exercise has been shown to have a positive impact on specific diseases such as diabetes, cancer, and hypertension. Physical activity helps to improve insulin sensitivity, making it easier for the body to regulate blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Exercise has also been linked to a lower risk of certain types of cancer, including breast, colon, and lung cancer. Additionally, engaging in regular physical activity can help to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of hypertension.
V. Social and Emotional Benefits of Regular Exercise
Regular exercise not only improves physical health but also has numerous social and emotional benefits. Engaging in exercise activities can foster social connections and boost self-confidence, leading to enhanced overall well-being. In this section, we will explore the role of exercise in fostering social interactions and the ways in which exercise enhances self-esteem and self-confidence.
A. Improved Social Connections
1. The role of exercise in fostering social interactions
Exercise provides opportunities for individuals to engage in social interactions and build connections with others. Whether it’s participating in group fitness classes, joining sports teams, or simply exercising with friends or family, physical activity can create a sense of community and camaraderie. Working out together allows individuals to bond over shared goals and experiences, fostering a supportive and motivating environment.
2. Exercise activities that promote social engagement
Various exercise activities encourage social engagement and interaction. Group fitness classes, such as Zumba, yoga, or cycling, offer a fun and social environment where participants can connect with like-minded individuals. Team sports, such as basketball, soccer, or volleyball, provide opportunities for teamwork, cooperation, and building relationships. Additionally, outdoor activities like hiking or jogging in parks can lead to chance encounters and social interactions with other fitness enthusiasts.
B. Boosted Self-Confidence
1. How exercise enhances self-esteem and self-confidence
Regular exercise has been shown to improve self-esteem and boost self-confidence. Engaging in physical activity releases endorphins, which are known as “feel-good” hormones. These endorphins contribute to a positive mood and a sense of accomplishment, leading to increased self-esteem. Additionally, exercise can help individuals achieve their fitness goals, which further enhances their self-confidence and belief in their abilities.
2. The psychological benefits of achieving fitness goals
Setting and achieving fitness goals through regular exercise can have profound psychological benefits. Accomplishing milestones, such as running a marathon, lifting heavier weights, or improving endurance, instills a sense of pride and accomplishment. This sense of achievement can spill over into other areas of life, boosting overall self-confidence and providing a sense of empowerment.
Aging is a natural process that brings about various changes in the body. As we age, our muscles tend to weaken, our bones become brittle, and our overall physical fitness declines. However, regular exercise can play a crucial role in promoting healthy aging and managing age-related conditions. In this section, we will explore the importance of exercise for healthy aging and discuss exercise recommendations for older adults.
A. Healthy Aging
1. The importance of exercise for healthy aging
Exercise is not only beneficial for maintaining physical fitness but also plays a vital role in promoting healthy aging. Regular physical activity can help older adults maintain muscle strength, improve balance and coordination, and enhance overall mobility. Engaging in exercise on a regular basis can also help prevent or delay the onset of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and osteoporosis.
Exercise has been shown to have numerous benefits for older adults, including:
- Improved cardiovascular health
- Increased muscle strength and endurance
- Better bone density and reduced risk of osteoporosis
- Enhanced flexibility and joint mobility
- Improved balance and coordination, reducing the risk of falls
- Enhanced cognitive function and reduced risk of dementia
- Improved mood and mental well-being
2. Exercise recommendations for older adults
When it comes to exercise, it’s important for older adults to engage in activities that are safe and suitable for their age and fitness level. The American Heart Association and the American College of Sports Medicine provide guidelines for exercise in older adults, which include the following recommendations:
- Aerobic exercise: Older adults should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week. This can include activities such as brisk walking, swimming, cycling, or dancing.
- Strength training: Older adults should engage in strength training exercises at least two days per week. This can involve using resistance bands, free weights, or weight machines to target major muscle groups.
- Balance exercises: Older adults should incorporate balance exercises into their routine to improve stability and reduce the risk of falls. This can include activities such as standing on one leg, heel-to-toe walking, or tai chi.
- Flexibility exercises: Stretching exercises should be included in the exercise routine to improve flexibility and range of motion. This can involve gentle stretching of major muscle groups, such as the shoulders, hips, and legs.
B. Managing Age-Related Conditions
1. How exercise helps in managing age-related conditions
Exercise can be particularly beneficial for older adults who are dealing with age-related conditions. Regular physical activity can help manage and improve various health conditions commonly associated with aging, including:
- Heart disease: Exercise can help lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Diabetes: Physical activity can help control blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity, making it an essential component of diabetes management.
- Osteoporosis: Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking or dancing, can help improve bone density and reduce the risk of fractures.
- Arthritis: Exercise can help reduce joint pain and stiffness, improve joint function, and enhance overall mobility in individuals with arthritis.
- Depression and anxiety: Regular exercise has been shown to boost mood, reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, and improve overall mental well-being.
2. Exercise modifications for individuals with specific health concerns
It’s essential for individuals with specific health concerns to consult with their healthcare provider or a qualified exercise professional before starting an exercise program. They can provide guidance on exercise modifications and tailor a program that suits their individual needs and abilities. Some common modifications for individuals with specific health concerns include:
- Cardiovascular conditions: Individuals with heart disease or other cardiovascular conditions may need to start with low-impact activities and gradually increase intensity. They may also need to monitor their heart rate and blood pressure during exercise.
- Joint problems: Individuals with joint problems, such as arthritis, may need to avoid high-impact activities and opt for low-impact exercises that are gentle on the joints. They may also benefit from exercises that improve joint flexibility and range of motion.
- Balance issues: Older adults with balance issues should focus on exercises that improve balance and stability, such as tai chi or yoga. They may also need to use assistive devices, such as a cane or walker, for added support.
- Chronic pain: Individuals with chronic pain should work with a healthcare provider or physical therapist to develop an exercise program that takes their pain into account. They may need to modify certain exercises or incorporate pain management strategies.
By making appropriate exercise modifications, individuals with specific health concerns can still reap the benefits of physical activity while minimizing the risk of injury or exacerbating their condition.
